- Bees
- Chickens
- Cows
- Deer
- Donkeys
- Elephants
- Frogs
- Geese
- Horses
- Lobsters
- Pigs
- Rabbits
- Rats
- Seals
- Sheep
- Turkeys
Elephants

Elephants belong to the family Elephantidae. They are the largest land animals in the world. They have the biggest brain (12 pounds), the thickest skin (1 inch) and the longest nose (their trunk is about 8 feet). Their waistline is about 16 feet.
Elephants belong to the order of Proboscidae, named for their trunks. Around 1 million years ago there were 11 species of proboscidean. Soon most of these species disappeared and only 3 survived: the mammoth (which became extinct 3,000-4,000 years ago) and the African and Asian elephants.
The African Elephant species is divided into two subspecies: the forest and the savannah. The forest elephant is smaller, has downward-pointed tusks, and smaller, rounder ears. The savannah elephant is larger and more widespread.
African elephants weigh up to 14,000 pounds. They have big ears, two-fingered trunks, concave backs, flat foreheads and large tusks. There are about 420,000 African elephants spread out over 37 African countries. They are native to a wide variety of habitats including open savannas and dense forests.

Asian elephants weigh up to 11,000 pounds. They have small ears, one-fingered trunks, convex backs, two bumps on their forehead and small tusks. There are about 35,000 Asian elephants spread out over 12 southeast Asian countries, including India. They live in large blocks of forest near water sources and grasslands.
Elephants have very versatile trunks, which are unique among living mammals. Their trunks are a combination of the upper lip and nose. They can use it to both manipulate tiny objects and tear down huge tree limbs. They also use their trunks to touch and greet other elephants. Female elephants frequently touch their babies. Elephants are able to draw up four gallons of water into their trunks before squirting it into their mouth to drink. They also use their trunks to spray water and dirt over their body in order to protect their skin from insect bites and sun exposure. When elephants sense danger, they will raise their trunks to smell any threat. They even use their trunks as snorkels when crossing deep rivers or lakes.

Elephants have a pair of upper tusks extending on either side of the trunk. Their tusks are always growing and can grow to be nine feet long. Most Asian female elephants don't grow tusks. Tusks consist of cartilaginous material and calcium salts and are the equivalent of incisor teeth. Elephants use their tusks for removing bark, digging for roots and as weapons.
Elephants have six large molars in each half of the upper and lower jaws. They use these teeth for grinding vegetation. They only use one at a time. When a tooth is worn out or broken, elephants will move their teeth forward and push it out. When the last molar moves forward, it must last the rest of the elephant's life. This usually happens around the age of 30. If this last molar doesn't last, the elephant won't be able to chew effectively and may starve.
Elephants use their large, soft and sensitive ears to cool off. The elephants' surface area is small compared to their mass, making it difficult to release body heat. Flapping their ears will cool the blood flowing through them, helping to regulate their body temperature. You can identify elephants by their ears which are unique.
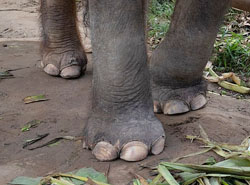
Elephants walk on their toes. The sole of each foot is made of a tough and fatty piece of tissue which acts as a shock absorber and helps elephants move silently. Their toes are buried inside the flesh of the foot and not all toes have toenails. African elephants have four toenails on the front feet and three on the back. Asian elephants have five on the front and four on the back.
Elephants are herbivores. They eat grasses, tree foliage, bark, bamboo, shrubs, roots and fruit. They also eat soil for its mineral content. They disperse undigested plant seeds through their dung, helping to cultivate plants. Full-grown African elephants will eat about 6 to 8 percent of their body weight in vegetation each day. They spend an average of 18 hours per day feeding. Asian elephants require less food because the food in their habitat is more diverse and of higher quality. Elephants can drink 67 gallons of water a day. They will dig for water during a drought.

The life span of an elephant is about 50-70 years.
Females and young males live in herds of about ten related adults and their offspring. The oldest and largest female, the matriarch leads the herd. She knows best where to find food and how to avoid danger. Males will leave the herds around their 13th year, and travel alone or in bachelor groups. Elephants travel around a lot in search of food.
Elephants communicate with body language and a variety of low-frequency sounds - trumpets, rumbles, squeaks, squeals and snorts. Their sounds can travel a mile or more. Some of their sounds are too low for humans to hear.
Female elephants begin reproducing at 11 years and continue through their fifties, giving birth to one calf every five years. Older and larger males dominate the breeding, winning the acceptance of females in heat. After a 22 month pregnancy, the female gives birth to a single calf which weighs more than 200 pounds and nurses for as long as four years. Baby elephants grow up surrounded by family members who help care for them. They sometimes suck on their trunks, the way human babies suck on their thumbs. They have milk tusks that fall out when they are about one year old.



